oem hs code black annealed wire
Understanding OEM HS Code for Black Annealed Wire
In the global trade landscape, the Harmonized System (HS) Code plays a crucial role in the classification of products for customs and trade purposes. Among various categories of products, black annealed wire is noteworthy for its applications in construction, manufacturing, and agricultural sectors. Understanding the OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) HS code for black annealed wire is essential for businesses engaged in importing or exporting these materials.
What is Black Annealed Wire?
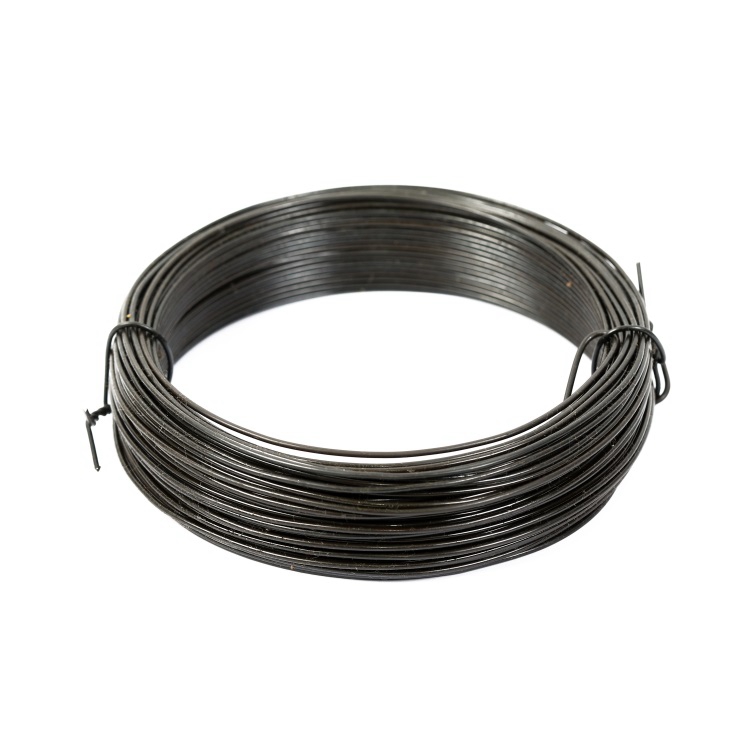
Black annealed wire is produced from low-carbon steel wire that has undergone an annealing process. This process involves heating the wire and then allowing it to cool slowly, which enhances its ductility and makes it more pliable. The black finish is a result of the oxide layer that forms during the heating process. This type of wire is primarily used for binding, tying, and construction purposes due to its strength and flexibility.
Importance of HS Codes
HS codes are standardized numerical codes that classify products in international trade. The World Customs Organization (WCO) has developed this system, and it is used by countries worldwide to streamline the process of tariffs, trade statistics, and customs procedures. For businesses engaged in international trade, accurate classification is crucial, as it can affect duties, taxes, and compliance with various regulations.
For black annealed wire, the HS code will vary based on its specific characteristics, such as its diameter and intended use. Typically, black annealed wire falls under the broader category of wire products made from iron or steel, which might have a specific area in the HS classification system.
Determining the Correct OEM HS Code
oem hs code black annealed wire

When determining the correct HS code for black annealed wire, businesses must consider several factors
1. Diameter of the Wire The diameter may affect the classification, as different thicknesses may fall under different code sections. 2. Type of Material While most black annealed wires are made of low-carbon steel, any additional coatings or treatments could influence the HS classification.
3. Application The intended use of the wire, whether for construction, agriculture, or manufacturing, can lead to different HS codes.
To correctly classify the wire, manufacturers and exporters should consult official customs resources or work with a customs expert. Using the right code is critical for compliance, as misclassification can lead to delays, fines, or challenges in customs clearance.
Challenges in Classification
One of the challenges companies face when classifying black annealed wire is the inconsistency in terminology and specifications. Different countries may classify similar products differently, leading to confusion. Additionally, updates to the HS system and changes in trade agreements can alter classification norms, making it necessary for businesses to stay informed.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the OEM HS code for black annealed wire is essential for companies involved in the manufacturing, exporting, or importing of this product. Accurate classification not only ensures compliance with trade regulations but also optimizes operations and helps in avoiding potential legal issues or financial penalties. As global trade continues to evolve, stakeholders in the wire manufacturing industry must remain vigilant and informed about HS coding to streamline their business processes effectively. By doing so, they can ensure that their operations run smoothly, contribute to efficient trade practices, and ultimately enhance their competitiveness in the global market.
-
The Durability and Versatility of Steel Wire
NewsJun.26,2025
-
The Best Iron Nails for Your Construction Projects
NewsJun.26,2025
-
Strengthen Your Projects with Durable Metal Stakes
NewsJun.26,2025
-
Get the Job Done Right with Duplex Nails
NewsJun.26,2025
-
Explore the Versatility and Strength of Metal Mesh
NewsJun.26,2025
-
Enhance Your Security with Razor Wire
NewsJun.26,2025